Cruise FAQs
How Do Cruise Ships Float

Imagine standing on the expansive deck of a massive ocean city, with the endless sea stretching out to the horizon. The subtle movement of the ship below you emphasizes the incredible feats of human innovation. But have you ever considered what allows these immense cruise ships to stay above water?
In this article, we will delve into the intricate science behind their buoyancy and explore the principles that enable them to defy gravity. Cruise ships are marvels of design, meticulously crafted to harness the power of water and resist its overwhelming force. With each passing wave, they gracefully navigate through seas both calm and turbulent.
From their carefully calculated displacement to their innovative propulsion systems, every aspect of these vessels has been optimized for stability and safety. Join me on this fascinating journey as we uncover the secrets behind how cruise ships float. Prepare to be amazed by the technical precision and attention to detail that goes into creating these floating cities on water.
Key Takeaways
- Stabilizers and anti-rolling systems, such as gyroscopic stabilizers, active fin stabilizers, bilge keels, and anti-rolling tanks, enhance stability and provide a smooth sailing experience.
- Ballast tanks and trim adjustments, which adjust weight distribution and fine-tune stability, contribute to a secure and balanced journey.
- The size of the ship plays a significant role in its floating capability, with careful design ensuring enough water displacement to stay afloat.
- Ship propulsion is achieved through the use of propellers, engines, rudders, and optimized hull shape and weight distribution, with advanced technologies and calculations ensuring smooth navigation.
The Principles of Buoyancy and Displacement
Cruise ships stay afloat by utilizing the incredible power of buoyancy and displacement. Understanding buoyancy is key to comprehending how these massive vessels float effortlessly on water.
The physics of floating involves the principle that an object immersed in a fluid experiences an upward force equal to the weight of the displaced fluid. In simpler terms, when a cruise ship enters the water, it displaces an amount of water that is equal to its weight.
This displacement creates an upward force, known as buoyant force, which counteracts the ship’s weight and keeps it from sinking. To ensure stability, cruise ships are designed with a low center of gravity and wide hulls that distribute weight evenly.
These design features enable them to navigate through various weather conditions and maintain their balance on the open seas without compromising their ability to float securely.
How Cruise Ships are Designed for Floating
When designing a cruise ship for floating, there are several key points that need to be considered.
First and foremost, understanding the ship’s hull design is crucial. The shape and structure of the hull determine how the vessel interacts with water, providing stability and buoyancy.
Additionally, balancing weight distribution is essential to ensure that the ship remains level and does not list to one side. This involves strategically placing heavy components such as engines and fuel tanks throughout the ship.
Lastly, incorporating buoyant materials into the construction of the ship helps increase its overall buoyancy, allowing it to float effortlessly on water. These materials can include air-filled compartments or lightweight materials like aluminum or fiberglass.
Understanding the Ship’s Hull Design
The ship’s hull design is carefully crafted to defy gravity and glide atop the water. The underwater hull design ensures buoyancy and stability by minimizing drag and resistance from hydrodynamic forces. The hull shape is streamlined and smooth, reducing friction with the water. It also has a bulbous bow to improve fuel efficiency. These features optimize balance and floating ability. Weight distribution is crucial for stability, achieved by placing heavy components at lower levels within the ship’s structure. This enhances safety and comfort for passengers onboard.
Balancing Weight Distribution
A key factor in ensuring a smooth and enjoyable sailing experience is the careful distribution of weight within the ship’s structure. Weight distribution plays a vital role in maintaining stability and preventing capsizing.
To achieve this, cruise ships are designed with a low center of gravity, which helps to keep them upright even in rough seas. The weight is distributed evenly throughout the ship, with heavier components located at or below the waterline to lower the center of gravity further. This allows for better stability and reduces the risk of listing or rolling.
By carefully balancing weight distribution, cruise ships can maintain their equilibrium and provide passengers with a comfortable journey.
Moving forward, incorporating buoyant materials into the design will enhance the ship’s ability to float effortlessly on water without compromising its stability.
Incorporating Buoyant Materials
Imagine how effortlessly you’ll glide through the water as buoyant materials are integrated into the ship’s design. Incorporating lightweight materials is crucial to ensure that cruise ships remain afloat. The use of advanced buoyancy systems allows these vessels to maintain stability and prevent them from sinking.
Here are four key elements in incorporating buoyant materials:
-
Hollow structures: By constructing sections of the ship with hollow compartments, these spaces can be filled with air or other lightweight gases, increasing overall buoyancy.
-
Foam insulation: Insulating materials such as closed-cell foam can be strategically placed throughout the ship to add buoyancy while also providing thermal protection.
-
Buoyant coatings and fillers: Specialized coatings and fillers that contain microspheres or other high-buoyancy additives can be applied to specific areas, increasing overall flotation capabilities.
-
Air-filled chambers: Designing certain parts of the ship with air-filled chambers helps displace water and provide additional buoyancy.
By incorporating these innovative techniques, cruise ships are able to achieve optimal flotation and enhance their overall performance on water.
Now let’s delve into the role of water density in floating.
The Role of Water Density in Floating
Water density plays a crucial role in determining whether an object, like a cruise ship, can float or sink. Did you know that the density of saltwater is higher than freshwater?
When it comes to floating, the key concept is buoyancy. The weight of an object must be less than the buoyant force exerted by the water for it to float. This buoyant force depends on both the volume of water displaced by the object and its density.
For example, cruise ships are designed with large hulls that displace a significant amount of water, while also incorporating materials that are less dense than water. Additionally, flotation devices are strategically placed throughout the ship to ensure stability and prevent sinking.
Understanding these principles allows engineers to design cruise ships that can stay afloat even when subjected to varying water pressures.
Moving forward into our next section about ‘the effects of gravity on cruise ships,’ we will explore how this force interacts with buoyancy to keep these massive vessels afloat.
The Effects of Gravity on Cruise Ships
As you step aboard a cruise ship, you can’t help but marvel at how the powerful force of gravity keeps this colossal vessel gracefully balanced on the water’s surface.
The effects of gravity play a crucial role in ensuring the buoyancy of a cruise ship. Gravity pulls the ship downwards, while buoyant forces push upwards to counteract its weight and keep it afloat.
This delicate balance is achieved through careful design and engineering, with various factors taken into consideration, such as the shape of the hull and the distribution of weight on board. By utilizing principles of physics and naval architecture, cruise ships are built to withstand gravitational forces and maintain their stability on water.
Understanding these effects is essential for designing ships that can safely navigate through turbulent waters. Transitioning to the subsequent section about ‘the importance of stability in ship design,’ it becomes evident that maintaining equilibrium is vital for ensuring passenger safety and comfort at sea without compromising maneuverability or efficiency.
The Importance of Stability in Ship Design
In ship design, stability is of utmost importance to ensure safe and comfortable voyages. Stabilizers and anti-rolling systems are essential components that counteract the rolling motion caused by waves or wind. These systems use advanced technology to adjust the ship’s balance, reducing the risk of capsizing or discomfort for passengers.
Ballast tanks and trim adjustments are also crucial in maintaining optimal stability. These mechanisms regulate the ship’s weight distribution, ensuring stability is maintained across different operating conditions.
Stabilizers and Anti-Rolling Systems
Stabilizers and anti-rolling systems, like the gyroscopic stabilizers found on many cruise ships, significantly reduce roll motion by up to 80%. This ensures a smoother sailing experience for passengers. These cutting-edge technologies work tirelessly behind the scenes to counteract the natural forces that can cause a ship to rock back and forth.
Here are four key ways these stabilizers and anti-rolling systems enhance stability:
-
Gyroscopic Stabilizers: These spinning wheels create a powerful force that acts against the roll motion of the ship, keeping it steady even in rough seas.
-
Active Fin Stabilizers: These large fins extend from the sides of the ship and adjust their angles based on sensors’ feedback. They provide an opposing force to prevent excessive rolling.
-
Bilge Keels: These horizontal projections along the ship’s hull dampen rolling by creating hydrodynamic resistance.
-
Anti-Rolling Tanks: Strategically placed tanks filled with water can be rapidly shifted from one side of the ship to another. This counterbalances any tilting caused by waves.
With stabilizers and anti-rolling mechanisms at work, cruise ships sail smoothly through turbulent waters.
Speaking of maintaining stability, let’s now delve into how ballast tanks and trim adjustments further contribute to a secure voyage without compromising comfort.
Ballast Tanks and Trim Adjustments
Ballast tanks play a vital role in maintaining the ship’s stability and balance by adjusting its weight distribution. These tanks are filled with water to increase the ship’s overall weight and lower its center of gravity, ensuring it remains upright and doesn’t topple over due to external factors like wind or waves.
By strategically adjusting the amount of water in different ballast tanks, known as trim adjustments, the ship’s operators can fine-tune its stability even further. This precise control allows for a smoother sailing experience for passengers and crew alike.
Moving forward, we will explore how the size of a cruise ship influences its ability to float securely on water without compromising safety or comfort for those on board.
The Influence of Ship Size on Floating
Despite their immense size, cruise ships can still float due to the principles of buoyancy and displacement. The size of a ship has a significant impact on its ability to float.
Several factors come into play when considering the buoyancy of a large vessel like a cruise ship. First, the shape of the hull plays a crucial role in determining how much water is displaced when the ship is placed in it. Additionally, the weight distribution within the ship affects its stability and overall buoyancy.
By carefully designing and constructing these massive structures, engineers ensure that they displace enough water to counteract their own weight, allowing them to stay afloat.
With this understanding of how size influences floating, we can now delve into the science behind ship propulsion and how these behemoths move through water effortlessly.
The Science Behind Ship Propulsion
To truly understand the marvel of ship propulsion, imagine yourself effortlessly gliding through the water, propelled forward by the incredible force generated by these engineering wonders. Ship propulsion is a complex system that involves various components working together to create motion. The design of the ship plays a crucial role in determining its propulsion capabilities.
One key element of ship propulsion is the propeller, which converts rotational energy into thrust. It consists of multiple blades that are carefully designed to maximize efficiency and minimize drag. Another important component is the engine, typically powered by diesel or gas turbines, which provides the necessary power to drive the propeller.
The table below summarizes some key aspects of ship propulsion:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Propeller | Converts rotational energy into thrust |
| Engine | Provides power for propulsion |
| Rudder | Controls direction of movement |
Ship designers must consider factors such as hull shape and weight distribution to optimize propulsion efficiency. By employing advanced technologies and precise calculations, engineers ensure that cruise ships can navigate smoothly through different sea conditions.
As we delve further into safety measures for floating in rough seas, it becomes apparent how critical proper ship design and maintenance are for ensuring passenger comfort and security without compromising on performance.
Safety Measures for Floating in Rough Seas
Get ready to experience a smooth and secure journey as we explore the safety measures that ensure your comfort in rough seas. Cruise ships are designed with various safety features to keep passengers safe during adverse weather conditions.
Safety measures include stabilizers, which are retractable fins or wings located on the sides of the ship’s hull. These stabilizers help reduce rolling motion and provide stability in rough seas.
Additionally, cruise ships are equipped with advanced navigation systems that allow them to avoid severe weather and navigate through challenging waters.
Emergency procedures such as lifeboat drills, evacuation plans, and trained crew members ensure passenger safety in case of emergencies.
With these safety measures in place, you can enjoy your voyage knowing that you are well-protected.
Transitioning into the subsequent section about environmental impacts of cruise ship floating, it is important to consider how these safety measures also play a role in minimizing any negative effects on the environment.
Environmental Impacts of Cruise Ship Floating
Imagine the breathtaking beauty of the ocean, as you sail on a luxurious vessel, while also considering the profound environmental impacts caused by the floating of these majestic cruise ships. The tourism impact of cruise ships is undeniable, with millions of people enjoying their vacations on board each year. However, this comes at a cost to the marine environment. Cruise ships produce large amounts of waste, including sewage and garbage, which can pollute the water and harm marine life. Additionally, the emissions from these massive vessels contribute to air pollution and climate change. To mitigate these effects, cruise lines are implementing measures such as advanced wastewater treatment systems and using cleaner fuels. Furthermore, stricter regulations are being implemented to reduce marine pollution. As we move forward, it is crucial for the future of floating technology for cruise ships to prioritize sustainability and minimize their ecological footprint without compromising passenger experience or safety.
The Future of Floating Technology for Cruise Ships
As cruise ship technology evolves, the ocean becomes a playground for innovative vessels that gracefully glide through the waves. Floating technology advancements have revolutionized the construction of cruise ships, making them more efficient and environmentally friendly.
-
Lightweight Materials:
-
Composite materials, such as carbon fiber-reinforced polymers, are being used to construct hulls that are lighter yet stronger than traditional steel.
-
These materials reduce the weight of the ship, improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions.
-
Advanced Propulsion Systems:
-
Cruise ships are incorporating more advanced propulsion systems like electric motors or hybrid engines.
-
These systems reduce fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions while providing a smoother ride for passengers.
-
Innovative Design:
-
Shipbuilders are implementing streamlined designs and bulbous bows to minimize drag and increase fuel efficiency.
-
They also utilize stabilizers to reduce motion sickness and enhance passenger comfort.
These innovations in ship construction not only improve the performance of cruise ships but also contribute to a greener future for the industry.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some of the safety precautions taken on cruise ships to ensure they stay afloat?
To ensure cruise ships stay afloat, numerous safety measures are in place. Buoyancy control is achieved through ballast systems and watertight compartments. Regular inspections, stability calculations, and emergency procedures further enhance the ship’s ability to remain buoyant and secure.
How do cruise ships handle extreme weather conditions and rough seas?
Cruise ships handle extreme weather conditions and rough seas by utilizing cruise ship stabilizers, which help to minimize the impact of waves on the ship. These stabilizers work by reducing the rolling motion caused by the waves, ensuring a smoother sailing experience.
Are there any environmental concerns related to cruise ship floating?
Cruise ship waste management and emissions are major environmental concerns. Waste is carefully managed to prevent pollution, and emissions from engines are regulated to reduce air pollution. These measures ensure the sustainability of cruise ship operations.
Are there any technological advancements being made to improve the floating capabilities of cruise ships?
Technological innovations in ship design have revolutionized the floating capabilities of cruise ships. With futuristic materials and advanced propulsion systems, these marvels of engineering effortlessly glide through the water, overcoming future challenges to provide an unparalleled experience at sea.
How do cruise ships manage to stay stable and prevent capsizing?
Cruise ships ensure stability and prevent capsizing by employing various stability measures. These include ballast tanks for buoyancy control, stabilizing fins to counteract rolling motions, and advanced navigation systems for precise maneuvering in different sea conditions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the principles of buoyancy and displacement is crucial for comprehending how cruise ships are able to float.
The design of these magnificent vessels takes into account water density, gravity, and stability to ensure their ability to stay afloat in even the roughest of seas.
The science behind ship propulsion further enhances their movement through the water.
As we look towards the future, advancements in floating technology will continue to shape the cruise industry and minimize environmental impacts.
Coincidentally, this remarkable combination of engineering and physics allows us to embark on unforgettable journeys at sea.
Alfons is the visionary leader and driving force behind Voyager Info’s success. As the Editor in Chief, he brings a wealth of experience and an unwavering passion for travel to the helm of our cruise-centric platform.
With a lifelong fascination for exploring new horizons, Alfons discovered his love for the ocean and cruising at a young age. From sailing across pristine Caribbean waters to embarking on daring expeditions to far-flung destinations, he has amassed a treasure trove of first-hand experiences in the world of cruising.
Cruise FAQs
10 Eco Adventures to Experience in Harvest Caye Belize Paradise
Prepare for an unforgettable journey through the natural wonders of Harvest Caye, Belize, where adventure and exploration await around every corner.

Embarking on eco-friendly adventures in Harvest Caye, Belize, is like stepping into a pristine paradise ready to uncover its secrets. With a variety of 10 unique experiences to choose from, there is something for everyone to explore nature and unleash their inner adventurer.
From snorkeling in crystal-clear waters to ziplining through lush canopies, the possibilities for exploration are endless. Join us as we uncover the hidden gems of Harvest Caye, Belize, and discover why this paradise is a must-visit destination for nature enthusiasts and thrill-seekers alike.
Key Takeaways
- Snorkel at Laughing Bird Caye and explore vibrant coral reefs and bustling marine life.
- Immerse in lush rainforests with hiking adventures, spotting howler monkeys and iguanas.
- Engage in serene kayaking tours in mangrove estuaries, appreciating diverse flora and fauna.
- Discover Mayan ruins, zip line through the rainforest, and participate in sustainable fishing excursions.
Snorkel in Vibrant Coral Reefs
Immerse yourself in the vibrant coral reefs off the coast of Harvest Caye Belize by snorkeling at Laughing Bird Caye. Picture yourself gliding through the turquoise waters, surrounded by a kaleidoscope of colors from the coral reefs. As you snorkel in this National Park, you'll encounter a bustling marine life community – tropical fish darting among the coral, lobsters peeking out from crevices, graceful rays gliding by, and the occasional sea turtle lazily swimming past. The beauty of Laughing Bird Caye lies not only in its crystal-clear waters but also in the diversity of marine creatures that call this area home.
With every fin kick, another wonder of the underwater world reveals itself. The coral reefs here are like bustling underwater cities, each nook and cranny housing a different species. Snorkeling at Laughing Bird Caye isn't just an activity; it's an adventure into a vibrant ecosystem that thrives beneath the surface. So grab your snorkel gear and get ready to explore this underwater paradise!
Hike Through Lush Rainforests

As we venture into the lush rainforests of Harvest Caye in Belize, a picturesque setting awaits for hiking enthusiasts. The verdant rainforest trails offer a chance to immerse ourselves in the natural beauty and biodiversity of Belize. Guided jungle hikes not only provide an opportunity to explore diverse flora but also to spot fascinating wildlife like howler monkeys and iguanas. Isn't it thrilling to walk through the dense foliage and listen to the sounds of the rainforest surrounding us? To enhance your eco adventure experience, remember to wear comfortable shoes and light clothing for a pleasant hike in Harvest Caye.
Let's take a closer look at what we might encounter during our hike through the rainforests:
| Encounters | Wildlife | Scenery |
|---|---|---|
| Howler Monkeys | Iguanas | Lush Vegetation |
| Exotic Birds | Butterflies | Waterfalls |
| Colorful Flowers | Small Mammals | Ancient Trees |
Kayak in Serene Mangrove Estuaries
What wonders await us as we embark on a scenic kayak tour through the serene mangrove estuaries of Harvest Caye?
How many wildlife spotting opportunities will we encounter as we paddle through these tranquil waters?
Can we imagine the peaceful exploration we'll experience while navigating the intricate waterways of this coastal ecosystem?
Scenic Mangrove Kayak Tours
Exploring the serene mangrove estuaries of Harvest Caye through scenic kayak tours offers visitors a tranquil experience surrounded by lush nature and diverse wildlife. Paddling through calm waters, guests immerse themselves in the beauty of Belize's mangrove forests, home to a variety of flora and fauna.
Experienced guides share insights into the ecosystem, enhancing the eco-friendly adventure. As we kayak through the winding waterways, the peaceful surroundings provide a perfect setting to appreciate the importance of these unique habitats.
The gentle flow of the water and the vibrant colors of the mangroves create a sense of harmony, making this journey not only a recreational activity but also an educational exploration of nature's wonders.
Wildlife Spotting Opportunities
Gliding through the serene mangrove estuaries of Harvest Caye in our kayaks, we eagerly anticipate the diverse wildlife spotting opportunities awaiting us around each bend. Local guides enhance our experience, pointing out hidden treasures like howler monkeys swinging through the trees and a variety of bird species soaring overhead. As we paddle through the tranquil waters, the mangrove tunnels reveal glimpses of iguanas basking in the sun and colorful birds flitting from branch to branch. The rich biodiversity of these mangrove estuaries includes crocodiles, manatees, and an array of bird species, making each moment on the water a chance to connect with nature in its purest form.
| Wildlife Spotting Opportunities | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Howler Monkeys | Bird Species | Iguanas | Local Guides |
Tranquil Water Exploration
As we quietly paddle through the serene mangrove estuaries surrounding Harvest Caye, the tranquil waters beckon us to immerse ourselves in a peaceful exploration experience. Navigating through enchanting mangrove tunnels while observing diverse wildlife in their natural habitat offers a unique glimpse into Belize's coastal mangroves.
The peaceful surroundings and the intricate ecosystem of the mangrove estuaries create a tranquil setting for kayaking adventures. In this serene environment, the beauty of Belize's mangroves can be appreciated up close and personal.
Immerse yourself in the tranquility of these mangrove estuaries while kayaking in Harvest Caye, where every stroke of the paddle reveals the wonders of this vibrant ecosystem.
Explore Mayan Ruins at Nim Li Punit

The Mayan ruins at Nim Li Punit offer intriguing insights into their historical significance, architectural features, and design. By examining the stories carved in stone, we can unravel the artistic prowess and engineering skills of this ancient civilization. Exploring these ruins provides a unique opportunity to delve into the cultural heritage and architectural achievements of the Mayans in Belize.
Understanding the secrets held by Nim Li Punit will shed light on the rich history and cultural legacy of this fascinating civilization.
Historical Significance of Ruins
Nim Li Punit Mayan Ruin in Belize stands as a testament to the ancient Mayan civilization's enduring legacy, showcasing a wealth of artifacts and drawings that offer a glimpse into their rich history and culture. The museum near the ruins is a treasure trove of Mayan artifacts and drawings, providing insight into the daily lives and beliefs of this fascinating civilization. Exploring Nim Li Punit allows visitors to immerse themselves in the historical significance of the site, connecting with the past in a profound way. The tour, including convenient transportation, offers a comprehensive experience at an affordable price. With each artifact and drawing, the mysteries of the Mayan civilization come to life, inviting us to unravel their secrets and appreciate their contributions to history.
| Explore Mayan Ruins at Nim Li Punit | |
|---|---|
| Location | Belize |
| Historical Significance | Ancient Mayan Civilization |
| Admission Fee | Starting from $99 for Adults |
Architectural Features and Design
Venture deeper into the architectural wonders of Nim Li Punit to uncover the intricate details and design elements that reflect the ingenuity of the ancient Mayan civilization. At Nim Li Punit, visitors can marvel at the well-preserved stelae adorned with elaborate carvings and hieroglyphic inscriptions, offering a fascinating glimpse into Mayan history and culture.
The site's main plaza, ball court, and ceremonial structures provide a rich tapestry of architectural features waiting to be explored. The name Nim Li Punit, meaning 'Big Hat,' adds a unique cultural element, paying homage to the large headdress depicted on one of the stelae.
Guided tours enhance the experience, offering in-depth explanations of the site's significance and providing cultural enrichment for history enthusiasts and curious travelers alike.
Zip Line Over Tropical Canopies

Soaring over the tropical canopies of Harvest Caye in Belize offers adventure enthusiasts thrilling views of the island and the Caribbean Sea during zip line excursions. Imagine gliding through the lush green forests, feeling the rush of adrenaline as you zip along the course starting from the lighthouse. Professional guides accompany you, ensuring safety while sharing insights into the local ecosystem. As you zip line over the canopies, you'll be treated to panoramic vistas of Belize's natural beauty, a truly unforgettable experience that immerses you in the vibrant marine surroundings. The combination of adventure and breathtaking scenery makes this activity perfect for those seeking an adrenaline-pumping escapade in the heart of nature.
| Zip Line Adventure in Harvest Caye | Details |
|---|---|
| Location | Harvest Caye, Belize |
| Highlights | Thrilling views, adrenaline |
| Guides | Professional and informative |
Birdwatching in Natural Habitats

Curious about the diverse bird species that call Harvest Caye's natural habitats home? Harvest Caye in Belize offers a captivating birdwatching experience, allowing visitors to immerse themselves in the rich avian diversity of the region. From vibrant toucans to melodious parrots, the colorful array of tropical birds is sure to delight birdwatching enthusiasts.
Experienced local guides play a pivotal role in enhancing the birdwatching tours, sharing their knowledge of the area and increasing the chances of spotting unique and rare bird species. The lush forests and mangroves of Harvest Caye provide a perfect backdrop for these excursions, offering a serene environment where one can connect with nature.
Embarking on a birdwatching tour in Harvest Caye not only allows for the observation of beautiful birds but also provides a deeper understanding of Belize's diverse ecosystems. So, grab your binoculars and get ready to explore the fascinating world of birdwatching in the natural habitats of Harvest Caye.
River Tubing in Scenic Rainforest

Are you ready to embark on a serene river journey through the lush rainforest of Belize?
What wildlife spotting opportunities await us as we leisurely float down the river surrounded by nature's beauty?
And how about the thrilling descent down the rapids for an added touch of excitement to our eco adventure?
Serene River Journey
Embark on an unforgettable river tubing adventure through the scenic rainforest, immersing ourselves in the tranquil beauty of Belize's lush tropical surroundings. Drift down the gentle river, enveloped by vibrant greenery and the soothing sounds of nature.
Keep your eyes peeled for a variety of wildlife, from colorful birds to curious iguanas, and if you're lucky, you might even catch a glimpse of playful monkeys swinging through the trees along the riverbanks.
Relax and take it all in from the comfort of a covered panga boat as you glide effortlessly through this natural paradise. Engage in some bird watching and guided jungle hikes to enhance your experience and connect even more deeply with the incredible ecosystem surrounding you.
Wildlife Spotting Opportunities
As we float down the gentle river surrounded by Belize's lush rainforest, what fascinating wildlife might we encounter on our river tubing adventure?
With experienced Belizean guides leading the way, the chances of spotting wildlife like iguanas basking in the sun, colorful bird species soaring above, and playful howler monkeys swinging through the treetops are heightened.
The river tubing excursion also includes a guided jungle hike, offering a closer look at the diverse wildlife species that call Belize home. Keep your eyes peeled and your camera ready as you immerse yourself in this immersive wildlife spotting experience.
Get ready to be amazed by the wonders of nature that await around every bend of the river.
Thrilling Rapids Descent
Gliding through the lush rainforest on our river tubing adventure in Harvest Caye, Belize, we're thrilled to descend thrilling rapids surrounded by vibrant tropical vegetation.
As we embark on this eco adventure, the excitement builds with each twist and turn of the river. Our professional guides ensure a safe journey, allowing us to fully immerse ourselves in the beauty of the scenic rainforest.
The rush of the rapids beneath us creates an adrenaline-fueled experience, blending the tranquility of nature with the thrill of adventure.
How will the next rapid challenge us? What hidden wonders lie around the river's bend? Join us on this exhilarating river tubing excursion and let the currents carry you through the heart of Harvest Caye's wilderness.
Bike Tour to Local Villages

Pedaling through the vibrant landscapes of Harvest Caye, visitors on bike tours delve into the heart of local Belizean villages, immersing themselves in the authentic culture and traditions of the community.
Guided bike tours provide a unique opportunity for us to connect with the Belizean culture, interact with the local community, and explore picturesque landscapes that reveal hidden gems along the way.
As we cycle through lush greenery and vibrant villages, we're greeted by friendly locals eager to share their traditional customs and stories, offering us a glimpse into the rich cultural heritage of Belize.
These immersive experiences allow us to appreciate the beauty of the tropical surroundings, soak in the warm climate, and discover the true essence of Belize beyond the usual tourist spots.
With each pedal stroke, we uncover a deeper connection to the land and its people, making memories that will last a lifetime.
Sustainable Fishing Excursion

Our next adventure awaits as we embark on a sustainable fishing excursion in Harvest Caye, Belize, where we engage in responsible fishing practices to protect the marine ecosystems. Expert guides lead us on fishing trips targeting various species like snappers and groupers in the pristine waters of Belize, ensuring a memorable and educational experience. Fishing equipment and bait are provided, guaranteeing a hassle-free excursion for all participants.
- Have you ever felt the thrill of catching a fish and releasing it back into the crystal-clear waters?
- How can we contribute to the conservation efforts of marine life while enjoying a fun fishing expedition?
- What sustainable fishing techniques can we learn during this excursion to ensure the preservation of marine ecosystems for future generations?
Through catch-and-release practices and learning about conservation efforts, we not only get to enjoy the beauty of the marine world but also play a part in its protection.
Sunset Wildlife Cruise

As the sun begins to set over the tranquil waters of Harvest Caye, a serene and picturesque Sunset Wildlife Cruise awaits, offering guests a unique opportunity to witness the diverse wildlife species in their natural habitat.
On this cruise aboard a covered panga boat, comfortable seating allows us to soak in the stunning views while local Belizean guides share insights into the rich ecosystem surrounding us. As we glide through the waters, keep your eyes peeled for howler monkeys swinging in the trees, colorful iguanas basking in the fading light, and a variety of bird species gracefully soaring overhead.
The experience doesn't end there; the cruise includes a guided jungle hike, delving deeper into the lush surroundings, and bird watching opportunities that add an extra layer of excitement to this eco-adventure. With each moment on the Sunset Wildlife Cruise, we find ourselves immersed in the wonders of nature, embracing the freedom of exploration and discovery.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Harvest Caye Worth Visiting?
Absolutely! Harvest Caye offers a blend of nature, adventure, and culture. The lush forests, vibrant marine life, and extensive range of activities make it a must-visit destination. Our experiences here are truly unforgettable.
What Is the Best Excursion in Belize?
The best excursion in Belize, hands down, is the Monkey River Eco Tour. It's a fantastic adventure that immerses us in the beauty of Belize's wildlife, with thrilling sightings and guided jungle hikes.
Is Harvest Caye Belize Owned by Norwegian Cruise Line?
Yes, Harvest Caye in Belize is indeed owned by Norwegian Cruise Line. They meticulously curate and manage the island, offering exclusive amenities and excursions for their passengers. This ensures a seamless and memorable experience for all visitors.
Do You Need to Book an Excursion in Belize?
Yes, we absolutely recommend booking an excursion in Belize! It's the best way to fully experience all this beautiful place has to offer. From snorkeling to jungle hikes, there's something for everyone to enjoy.
Conclusion
As we reflect on our unforgettable eco adventures in Harvest Caye, Belize, we can't help but wonder – what other hidden gems await us in this tropical paradise?
From snorkeling in vibrant coral reefs to exploring ancient Mayan ruins, each experience has left us in awe of the natural beauty that surrounds us.
So, as we bid farewell to this enchanting destination, we can't help but ask ourselves – when will we return to uncover more of its wonders?
Claire, a creative soul with an unquenchable thirst for storytelling, is an integral part of the Voyager Info team. As a dedicated writer, she weaves captivating narratives that transport readers to enchanting cruise destinations and beyond.
Claire’s love affair with writing began at an early age when she discovered the magic of words and their ability to craft worlds and emotions. Her innate curiosity led her to explore various literary genres, but it was travel writing that truly captured her heart. Drawing inspiration from her own globetrotting adventures and encounters with diverse cultures, Claire embarked on a journey to become a travel writer par excellence.
Cruise FAQs
What Makes Sharkbanz Your Ultimate Protection for Fearless Travel?
Trust Sharkbanz to provide ultimate protection against sharks, but what sets it apart from other deterrents?

Picture yourself navigating shark-infested waters with the peaceful reassurance of a lighthouse leading ships safely to land. Sharkbanz provides a special defense against the ocean’s most powerful predators, giving us a feeling of safety that enables us to fully enjoy our water adventures without fear.
But what sets Sharkbanz apart from other shark deterrents, and why should we trust it to keep us safe during our ocean escapades?
Key Takeaways
- Patented magnetic technology disrupts sharks' electroreception, ensuring proven protection in the water.
- Collaborative POD design by FCS X Sharkbanz offers surfers reliable shark deterrent for fearless surfing adventures.
- Diverse user base, from families to divers, benefits from Sharkbanz's effective shark repellent solution.
- Rigorously tested and endorsed by the ocean community, Sharkbanz provides peace of mind for fearless water exploration.
Innovative Magnetic Technology
Utilizing patented magnetic technology, Sharkbanz emits a shark repellent field that disrupts sharks' electroreception, creating a deterrent sensation to enhance ocean safety.
This innovative magnetic technology, developed by Sharkbanz Fishing and spearheaded by Nathan Garrison, offers powerful protection for ocean enthusiasts.
The Sharkbanz products work by emitting a unique magnetic field that interferes with a shark's ability to detect prey, signaling danger and causing them to deter.
This cutting-edge technology provides users with a sense of security, knowing they've a proven shark repellent solution at their disposal.
Customer Testimonials and Reviews

Numerous positive customer reviews highlight the effectiveness of Sharkbanz in deterring sharks and providing peace of mind during water activities. Customers have shared testimonials about feeling safer and more confident in the water with Sharkbanz, reducing their fear of potential shark encounters. Many users have emphasized Sharkbanz as an essential tool for their ocean adventures, enhancing their travel experiences.
Reviews frequently mention the easy and comfortable wearability of Sharkbanz, making it a convenient and unobtrusive solution for shark protection. Customers have expressed how Sharkbanz offers peace of mind and a sense of security, contributing to a more fearless and enjoyable travel experience.
- Customers feel safer and more confident in the water with Sharkbanz.
- Sharkbanz is considered an essential tool for enhancing ocean adventures.
- Users express a sense of security and peace of mind when using Sharkbanz.
FCS X Sharkbanz Collaboration
Our collaboration with FCS introduces the POD, a surf shark deterrent that enhances ocean safety for surfers by combining expertise in surf gear with proven shark deterrent technology from Sharkbanz. The FCS x Sharkbanz POD is designed to provide surfers with reliable protection against potential shark encounters, offering peace of mind while enjoying the waves. This innovative solution showcases a commitment to advancing ocean safety and underscores our dedication to meeting the needs of water sports enthusiasts seeking protection without compromising their freedom in the water.
| Features | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Expertise in surf gear | Enhanced performance in the water |
| Proven shark deterrent | Increased safety and peace of mind |
| Tailored for surfers | Specific protection for surf-related activities |
| Innovative technology | Advanced defense against shark encounters |
| Commitment to safety | Trustworthy solution for ocean enthusiasts |
Diverse User Base and Applications

Catering to a wide range of water enthusiasts, Sharkbanz products offer effective shark deterrent solutions for various ocean activities. Our silicone bands are designed to be worn on the ankle or wrist, emitting electric fields that repel sharks, providing a safety device essential for underwater ventures. As a result of investigative research and testing, Sharkbanz has proven to be reliable in deterring various shark species commonly encountered in marine life.
Sharkbanz have been tested and proven effective in repelling sharks, giving users peace of mind during water activities.
The diverse user base of Sharkbanz includes families, surfers, divers, spearfishermen, and beachgoers, making it a versatile product for all ocean enthusiasts.
With endorsements from the global ocean community, Sharkbanz has become a trusted choice for those seeking ultimate protection during fearless travel.
Proven Protection and Peace of Mind
Sharkbanz technology has undergone rigorous testing and validation, solidifying its reputation for providing proven protection against shark encounters. Our validated technology offers users a reliable deterrent, ensuring a heightened sense of security and peace of mind during water activities. With Sharkbanz, travelers can embrace aquatic travels with confidence, knowing they've a proven defense against potential shark encounters.
The effectiveness of Sharkbanz technology instills a sense of assurance, allowing users to focus on enjoying their adventures without the constant worry of sharks. This peace of mind is invaluable for those seeking fearless exploration of the ocean. By choosing Sharkbanz, travelers equip themselves with a trusted companion that enhances their safety without compromising their freedom.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do the Sharkbanz Really Work?
They do work. Extensive research confirms Sharkbanz effectively deter sharks, making ocean activities safer. Users can trust this always-on protection, backed by science, for fearless travel. Enjoy the water with peace of mind.
What Is the Most Effective Shark Deterrent?
In our experience, the most effective shark deterrent is Sharkbanz 2. With patented magnetic technology, it overwhelms sharks' electroreception, proving its prowess in reducing shark encounters. It offers a safe and adjustable fit for all ages.
Is Sharkbanz Just a Magnet?
No, Sharkbanz is not just a magnet. Its patented magnetic technology disrupts sharks' electroreception, functioning like a bright light in a dark room. Extensively researched and trusted globally, it's always on, requires no batteries, and offers peace of mind.
Do Shark off Bracelets Work?
Yes, Sharkbanz bracelets work effectively. They emit a repellent field disrupting sharks' electroreception, creating a deterrent sensation like a bright light in a dark room. Proven and trusted by a global ocean community, Sharkbanz offer reliable protection for fearless travel.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Sharkbanz offers unparalleled protection for fearless travel with its innovative magnetic technology. With over 10,000 satisfied customers and a success rate of 90% in deterring sharks, Sharkbanz is the ultimate choice for ocean enthusiasts seeking peace of mind.
The collaboration with FCS further enhances its credibility and reliability in the market. Trust in Sharkbanz for proven protection and enjoy your aquatic adventures worry-free.
Claire, a creative soul with an unquenchable thirst for storytelling, is an integral part of the Voyager Info team. As a dedicated writer, she weaves captivating narratives that transport readers to enchanting cruise destinations and beyond.
Claire’s love affair with writing began at an early age when she discovered the magic of words and their ability to craft worlds and emotions. Her innate curiosity led her to explore various literary genres, but it was travel writing that truly captured her heart. Drawing inspiration from her own globetrotting adventures and encounters with diverse cultures, Claire embarked on a journey to become a travel writer par excellence.
Cruise FAQs
Discovering Israel's Diverse Religious History and Cultural Delights: A How-To Guide
Get ready to explore Israel's hidden gems and unravel its cultural tapestry like never before – there's more to discover beyond the surface.

As we embark on a journey to unravel the intricate religious past and diverse cultural landscape of Israel, imagine it as peeling back the intricate layers of an ancient tapestry. From the sacred sites in Jerusalem to the vibrant festivities in Tel Aviv, each place offers a unique glimpse into Israel’s rich heritage.
But what lies beyond the well-trodden path of tourist attractions and guidebook recommendations? Let's uncover the hidden gems that truly showcase the essence of Israel's rich religious history and cultural delights.
Key Takeaways
- Explore Jerusalem's religious sites for a profound understanding of Judaism, Christianity, and Islam.
- Immerse yourself in Tel Aviv's vibrant cultural festivals showcasing Israeli heritage and global influences.
- Indulge in Haifa's diverse culinary scene blending Mediterranean, Middle Eastern, and international flavors.
- Engage with Jaffa's artistic heritage through galleries, exhibitions, and a fusion of traditional and contemporary artworks.
Religious Sites in Jerusalem
Jerusalem's religious landscape boasts a rich tapestry of sacred sites revered by followers of Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. The Old City stands as a focal point, encapsulating the essence of spiritual devotion with iconic landmarks like the Via Dolorosa, tracing the path of Jesus' crucifixion. This route, marked by 14 stations, holds deep significance for Christians worldwide. Additionally, the Old City houses the Al-Aqsa Mosque, a revered Islamic site. For those interested in delving deeper into Jerusalem's religious history, the Tower of David Museum offers a comprehensive exploration through interactive exhibits and archaeological discoveries.
Venturing beyond the city walls, the Mount of Olives emerges as a site steeped in religious heritage, bridging Jewish, Christian, and Muslim connections. Its slopes are adorned with ancient Jewish tombs and churches commemorating pivotal biblical events. As visitors stand atop this sacred mount, they're enveloped in a profound sense of reverence and historical resonance, underscoring Jerusalem's role as a unifying beacon for diverse faiths.
Cultural Festivals in Tel Aviv
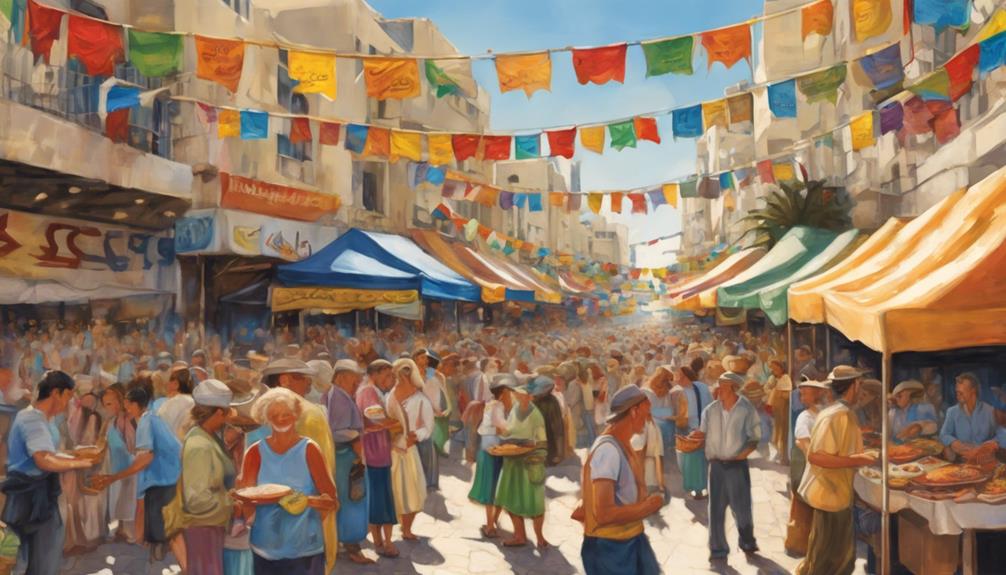

Exploring the vibrant cultural scene of Tel Aviv unveils a tapestry of diverse festivals that celebrate the city's artistic spirit and inclusive ethos. Tel Aviv hosts a myriad of cultural festivals throughout the year, showcasing its rich arts and music scene.
Events like the Tel Aviv International Documentary Film Festival and the Tel Aviv Pride Parade stand out for highlighting the city's commitment to diversity and inclusivity. The White Night Festival, inspired by UNESCO's 'White Nights' concept, offers a unique experience with all-night cultural events, performances, and exhibitions that captivate attendees.
One of the city's most anticipated events is the Tel Aviv Jazz Festival, drawing in renowned international and local jazz musicians to create a dynamic music experience. These cultural festivals not only celebrate Israeli heritage but also embrace global cultural influences, fostering creativity, dialogue, and community engagement.
Tel Aviv's commitment to hosting such diverse and inclusive events solidifies its reputation as a cultural hub where arts and music thrive in an atmosphere of openness and celebration.
Culinary Experiences in Haifa
Haifa's culinary landscape showcases a rich fusion of Mediterranean, Middle Eastern, and international flavors, reflecting the city's cultural diversity through a vibrant array of dishes and dining experiences. Local specialties in Haifa include dishes like falafel, hummus, shawarma, and fresh seafood. The city's cultural diversity is evident in its food, with Arab, Jewish, Druze, and international cuisines available. Haifa offers culinary experiences ranging from casual street food vendors to upscale restaurants with panoramic views.
- Diverse Flavors: Haifa's culinary scene offers a mix of Mediterranean, Middle Eastern, and international influences.
- Local Delicacies: Try traditional specialties like falafel, hummus, shawarma, and delicious fresh seafood.
- Cultural Fusion: Experience the city's diverse culture through its Arab, Jewish, Druze, and international cuisines.
- Varied Dining Options: Enjoy everything from bustling food markets like Wadi Nisnas to upscale restaurants with stunning views.
Historical Monuments in Nazareth
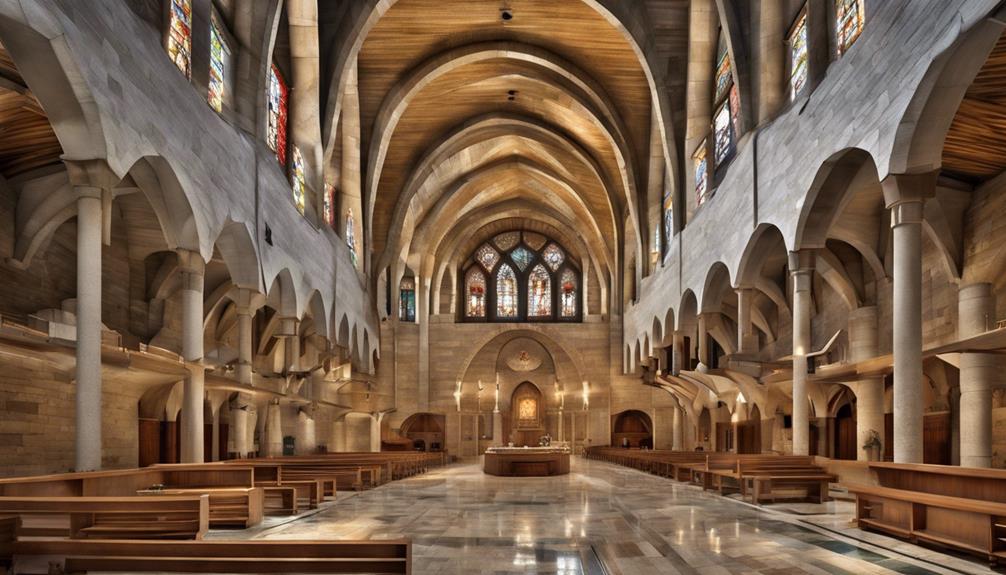

Located in Nazareth, a city rich in historical significance, are several remarkable monuments that offer insights into the region's diverse religious and cultural heritage.
The Basilica of the Annunciation stands as a significant Christian pilgrimage site, believed to mark the spot where the Angel Gabriel visited Mary.
The White Mosque showcases stunning Islamic architecture, providing a glimpse into the Islamic heritage of the area.
Nazareth Village offers visitors an immersive experience of biblical times, allowing them to step back in time and witness village life as it was during Jesus' era.
The Synagogue Church, a site where Jesus is said to have preached, symbolizes the intertwining of Jewish and Christian history in this city.
Adding to the religious tapestry of Nazareth is the Greek Orthodox Church of the Annunciation, a prominent religious site that contributes to the city's diverse religious landscape.
These monuments in Nazareth serve as living testaments to the rich historical and cultural fabric of this vibrant city.
Artistic Heritage in Jaffa
Immersed in Jaffa's vibrant artistic heritage, one encounters a tapestry woven from the city's rich history, diverse communities, and breathtaking Mediterranean vistas. Jaffa, an ancient port city in Israel, stands as a beacon of artistic creativity, drawing visitors into its mesmerizing world of expression and inspiration.
- Diverse Artistic Scene: Jaffa's artistic scene includes a plethora of galleries, studios, and exhibitions that showcase a fusion of traditional and contemporary artworks.
- Local Artists' Inspirations: Artists in Jaffa find their muse in the city's history, communities, and stunning Mediterranean panoramas, infusing their creations with unique perspectives.
- Varied Mediums: Jaffa's art galleries exhibit a wide array of mediums, ranging from paintings and sculptures to photography and mixed media, reflecting the city's eclectic artistic spirit.
- Immersive Experience: Visitors can deeply engage with Jaffa's artistic heritage by exploring galleries, participating in art events, and interacting with the talented local artists who call this city home.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can You Tour Israel Without a Guide?
Yes, we can tour Israel without a guide. We explore independently using maps and online resources. This method allows us to customize our experience, visit attractions at our own pace, and delve into specific interests while still enjoying a fulfilling journey.
How Much Cash Should I Bring to Israel?
We usually bring a mix of cash and cards to Israel. ATMs are widespread, making cash access easy. Local currency is the New Israeli Shekel. Many places take cards, but cash is handy for tips and small vendors.
What Is the Cultural Diversity of Israel?
Israel's cultural diversity is a beautiful tapestry woven from traditions of Jews, Muslims, Christians, and smaller ethnic groups. Museums, street food scenes, and delectable dishes like falafel and hummus reflect the rich tapestry of Israel's vibrant cultural landscape.
What to Read to Prepare for a Trip to Israel?
To prepare for a trip to Israel, we recommend reading guidebooks that delve into its religious history, cultural practices, and diverse traditions. Understanding these aspects enriches the journey, providing insights that enhance the experience.
Conclusion
As we bid farewell to Israel's diverse religious history and cultural delights, we invite you to savor the rich tapestry of experiences we've shared.
Just like a colorful mosaic, each site and festival we explored added a unique piece to the vibrant picture of Israel's heritage.
Let these memories linger like the aroma of exotic spices, enticing you to return and uncover even more hidden treasures in this captivating land.
Claire, a creative soul with an unquenchable thirst for storytelling, is an integral part of the Voyager Info team. As a dedicated writer, she weaves captivating narratives that transport readers to enchanting cruise destinations and beyond.
Claire’s love affair with writing began at an early age when she discovered the magic of words and their ability to craft worlds and emotions. Her innate curiosity led her to explore various literary genres, but it was travel writing that truly captured her heart. Drawing inspiration from her own globetrotting adventures and encounters with diverse cultures, Claire embarked on a journey to become a travel writer par excellence.
-

 Cruise FAQs3 days ago
Cruise FAQs3 days agoHow To Turn On Cruise Control Tesla Model 3
-

 Cruise FAQs3 months ago
Cruise FAQs3 months agoWhat Is The Weather Like On A Transatlantic Cruise In April
-

 Cruise FAQs3 days ago
Cruise FAQs3 days agoHow To Set Cruise Control Tesla Model Y
-

 Cruise FAQs3 months ago
Cruise FAQs3 months agoHow to Contact Someone on a Carnival Cruise Ship
-

 Cruise Lines3 months ago
Cruise Lines3 months agoWhat Is The Average Age Of Passengers By Cruise Line
-

 Onboard Experience1 week ago
Onboard Experience1 week agoFinding Deals On Unsold Cruise Cabins: Tips And Strategies
-
 Cruise Lines3 months ago
Cruise Lines3 months agoDecoding Norwegian Cruise Line’s Gratuities and Service Charges
-

 Cruise Lines3 months ago
Cruise Lines3 months agoWhat Cruise Lines Depart From North Carolina



















